In Windows 8 Microsoft removed the user interface for creating and viewing the Windows Experience index on the System Control Panel. Even though it is not an accurate benchmark of a computer it does give some basic and especially quick indication of performance of some of the major parts of a computer.
Below, I show two ways of creating and viewing the Windows Experience Index. Neither are difficult to perform, especially, if you are used to entering commands at a command line. These methods work in Windows 8, Windows 8.1 and Windows 10.
Method 1
Open an elevated command prompt (Command prompt (Admin)) and enter:
|
1 |
winsat prepop |
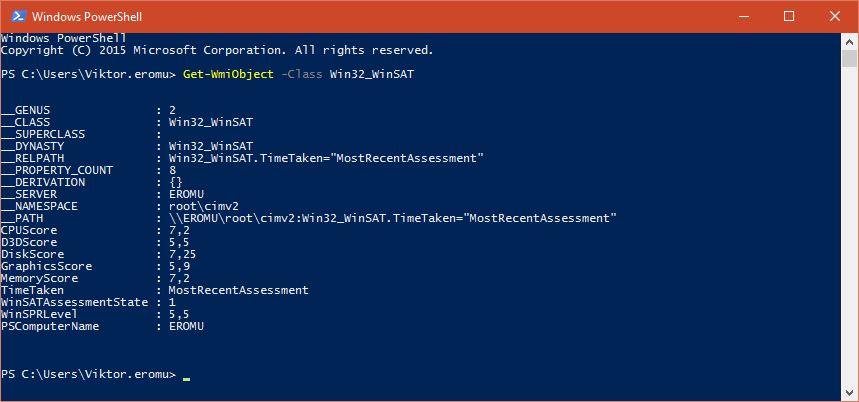
Once the command finished running (a couple of minutes, depending on your hardware setup), open Windows Powershell and enter:
|
1 |
Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_WinSAT |
Method 2
First, delete the whole content of the following folder:
|
1 |
C:\Windows\Performance\WinSAT\DataStore |
Then, at an elevated command prompt enter:
|
1 |
Winsat formal -restart |
Once the command finished running (a couple of minutes, depending on your hardware setup), go to the folder that you emptied in the first step and locate the file that is similar to this: 2015-12-10 11.29.23.105 Formal.Assessment (Initial).WinSAT.xml
Open the file in an XML viewer. Internet Explorer is a good choice for this purpose. Towards the beginning of the file locate the WinSPR element: